NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages


Written by Katya Richardson
Share this article
Growing in adoption, many people are delving into the world of cryptocurrency mining; earning rewards for verifying transactions and creating new blocks on the blockchain network through solving mathematical riddles. But what exactly is a blockchain, how does blockchain mining work and how can you get started? In this post, we will be examining all things about blockchain and everything you need to know to start mining.
As you may have guessed from the name, blockchains are made up of a series of ‘blocks’ and ‘chains.’ These ‘blocks’ store data of recent transactions occurring on the network that are yet to be validated and represent an explicit encryption of a particular code authentication on the network software with the ‘chains’ connecting blocks together. Once a block is verified, that block is closed with a new one created for new transactions that are to be validated next.
Mining is the term for this transaction-verification procedure explained above and is called “mining” because it is comparable to the mining of commodities like gold and silver, which involves a lot of work and resources but has a finite supply, thus the annual amount of gold produced essentially stays the same.
The people who secure and verify these transactions are known as blockchain miners, and they operate in a maze of computational hardware and software such as adding Bitcoin transaction data to Bitcoin’s global public ledger of past transactions, with the primary goal of authenticating the movement of Bitcoin from one computer in the network to another.
At its core, the term ‘blockchain mining’ is used to describe the process of adding transaction records to the blockchain. This process of adding blocks to the blockchain is how transactions are processed and how cryptocurrency moves around securely. Additionally, the procedure has a reward. The mining process is not managed by a single user, rather, several users compete for the benefits via unified authentication. Cryptocurrencies are added as a bonus after each mining accomplishment.
With the complexity of work in the mining process, working with a regular desktop or PC is not feasible. The blockchain mining process requires unique sets of computer hardware and software that will meet the necessary level of skill. The mining process can be divided into three categories:
If you’re new to the world of cryptocurrency, understanding the differences between individual mining, pool mining, and cloud mining is essential. Explore the advantages and disadvantages of the different methods commonly used.
New blockchain transactions are transferred to a pool called a memory pool when they are made. It is the responsibility of a miner to check the validity of these pending transactions and group them into blocks. After that, the miner tries to turn this candidate block into a valid, confirmed block. The miner needs a lot of computing resources to solve a challenging problem in order to accomplish this. However, the miner receives a block reward made up of fresh coins for each successfully mined block. Let’s take a closer look at how it works.
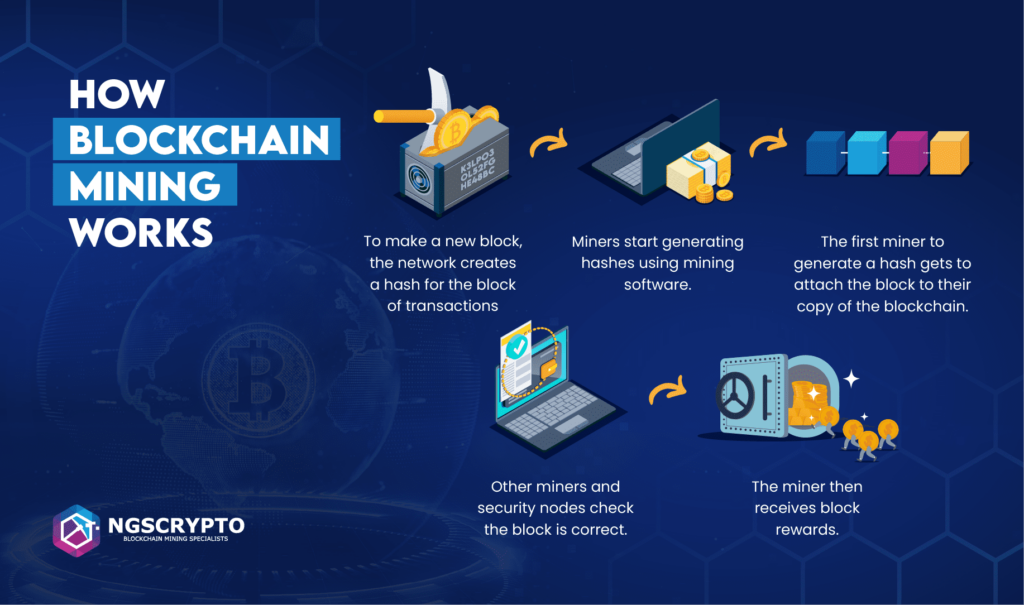
The miners work in a maze of computational hardware and software such as adding Bitcoin transaction data to Bitcoin’s global public ledger of past transactions, with the primary goal of authenticating the movement of Bitcoin from one computer in the network to another.
The miners will get paid after confirming a fresh block of Bitcoin transactions, Bitcoin miners receive incentives that are paid in Bitcoin. As of May 2020, the price is 6.25 bitcoins per block, which are awarded to miners who successfully validate a block, The price of Bitcoin may change once more in 2024, depending on events like the Bitcoin halving.
Now that you have a better understanding of blockchain mining, you might be wondering about its practical application, especially in specific regions like Australia. If you’re based in Australia or interested in the Australian crypto mining landscape, our article Is It Worth Mining Crypto in Australia? offers an in-depth look into the feasibility, costs, and benefits of mining in this region. This guide will provide you with a localized perspective and help you assess if mining is a viable venture in the Australian context.
The information presented on this website is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind.
NGS Crypto is an authorised reseller of NGS Group blockchain mining packages. The information presented on this website (https://ngscrypto.com) is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind. Before making an investment in crypto assets, you should consider seeking independent legal, financial, taxation or other such professional advice to check how the information on this website relates to your unique circumstances. NGS Crypto is not liable for any loss caused, whether due to negligence or otherwise arising from the use of, or reliance on, the information provided directly or indirectly, by use of this website. You can view our full terms & conditions by clicking here.
NGS Crypto is not affiliated, associated, authorized, endorsed by, or in any way officially connected with this NGS Super (ABN 73 549 180 515).
© 2024 NGS Crypto
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |