NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages


Written by Katya Richardson
Share this article
In the world of cryptocurrencies, the practice of crypto mining has undergone a remarkable transformation, shaping a multifaceted terrain; weaving together technology and strategy. As global adoption of mining increases, so does curiosity surrounding the topic with many people wanting to take a deep dive into the topic, understand it and how they can get started and capitalise on it.
Understanding this landscape requires a look back at the evolution of cryptocurrency mining. Over the years, there has been a noticeable shift in how mining is approached. If we delve deeper into the current trends, the variation in mining methods becomes evident.
Whilst some miners prefer working independently through solo mining, others collaborate in pools or groups for better efficiency and rewards. With technological advancements, cloud mining has emerged as a popular choice, eliminating the costs needed for physical hardware.
This article will breakdown the different types of cryptocurrency mining and explore the advantages and disadvantages of the different methods commonly used.
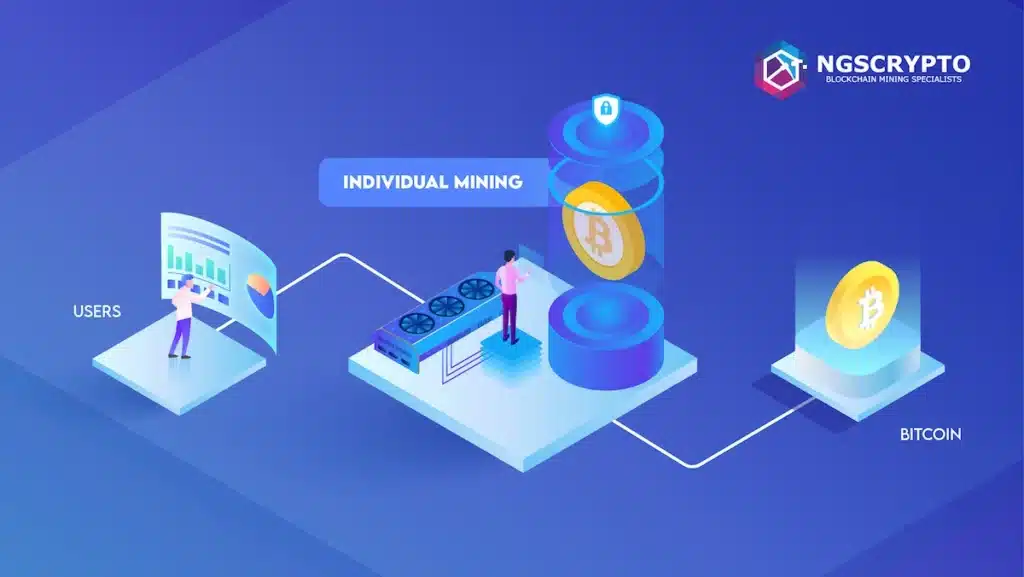
In individual mining, the user has to register themself as a miner. When a transaction occurs, the blockchain network presents all miners with a cryptographic challenge that the miners must solve. The one who solves the complex mathematical problem first wins. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
This puzzle-solving ensures security and decentralisation in the network, and miners will receive cryptocurrency as a reward for their efforts.
While individual mining centers around the ‘Proof of Work’ approach, there’s another consensus mechanism that’s gaining traction: Proof of Stake. Understand the nuanced differences and evaluate which might be the future of blockchain in our comprehensive analysis of PoW vs. PoS.
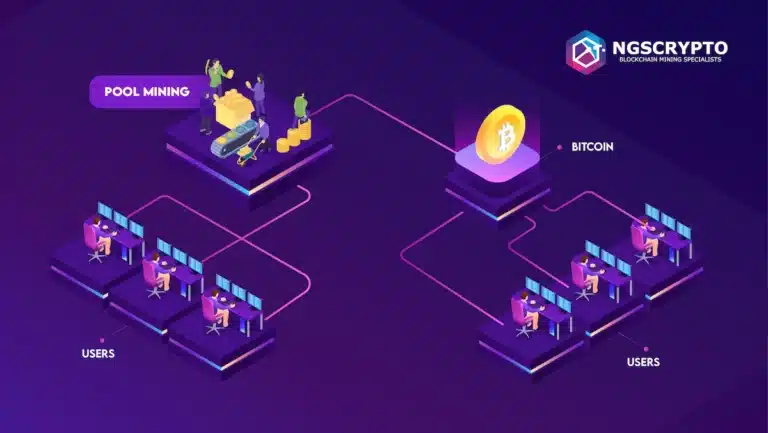
A mining pool is a group of cryptocurrency miners who collaborate to improve their chances of finding a block. They achieve this by sharing their computing power. If the mining pool achieves success and earns a reward, typically in the associated cryptocurrency, this bounty is distributed among the pool members according to the ratio of processing power or work contributed by each person. Individual miners might need to provide evidence of work to claim their rewards.
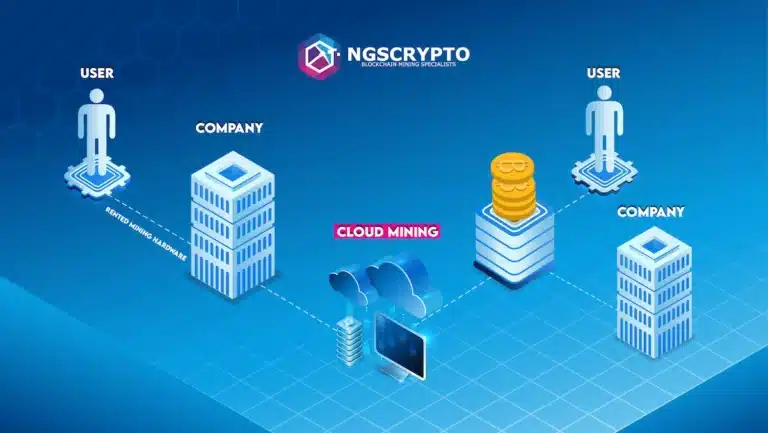
Cloud mining is an alternative to the traditional cryptocurrency mining system. Instead of spending money on expensive equipment and dealing with its maintenance yourself, you can now rent computing power from software companies with warehouses of powerful processors.
Rather than buying costly equipment, you can lease mining equipment from a distinct cloud mining firm situated anywhere globally. Cloud mining is only for proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum that rely on computational power.
To summarise, Cloud mining is a method of participating in cryptocurrency mining without having to acquire or operate mining hardware. Users instead pay a fee to rent mining capacity from a business that owns and operates the mining hardware and process. When the company and its users successfully mine a block using leased mining equipment, they divide the profits.
Our journey through the evolution of crypto mining methods has revealed a diverse landscape, shaped by changing trends and technological advancements. From individuals tackling cryptographic puzzles to collaborative efforts within mining pools and the convenience of cloud mining, each approach comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
The key takeaway is the importance of carefully considering the mining method that best aligns with your personal goals and available resources. By grasping the intricacies of these mining techniques, you can confidently embark on your cryptocurrency mining adventure, contributing to the security and vitality of the blockchain network while enjoying the potential rewards it brings.
The information presented on this website is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind.
NGS Crypto is an authorised reseller of NGS Group blockchain mining packages. The information presented on this website (https://ngscrypto.com) is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind. Before making an investment in crypto assets, you should consider seeking independent legal, financial, taxation or other such professional advice to check how the information on this website relates to your unique circumstances. NGS Crypto is not liable for any loss caused, whether due to negligence or otherwise arising from the use of, or reliance on, the information provided directly or indirectly, by use of this website. You can view our full terms & conditions by clicking here.
NGS Crypto is not affiliated, associated, authorized, endorsed by, or in any way officially connected with this NGS Super (ABN 73 549 180 515).
© 2024 NGS Crypto
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |