NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group Blockchain Mining Packages


Written by Katya Richardson
Share this article
In this digital era, it seems that everyone has now heard of Bitcoin and Bitcoin mining, but how many actually understand how it works? With the rising costs of living, many people are searching for different ways to supplement their salary with a passive income, resulting in an increase in searches for ‘how to mine Bitcoin.’ This article will explore, in-depth, what Bitcoin mining is, how it works and how you can get started.
In simple terms, Bitcoin mining can be thought of as “transaction processing” that secures the network and validates all Bitcoin transactions. To explain this in technical terms; Bitcoin mining is the process of confirming information in a blockchain block by creating a cryptographic solution to a complex algorithm, ensuring that:
The individuals who perform this validation are called miners. They work within a complex network of computational hardware and software, authenticating the movement of Bitcoin from one computer to another by adding transactional data to Bitcoin’s global public ledger.
Mining takes tremendous computational power and costly equipment so why do people do it? People mine Bitcoin for one simple reason: to earn Bitcoin. Miners are paid a reward for solving these complex cryptographic puzzles in the form of Bitcoin itself, which is then released into circulation.
Bitcoin was the first decentralised cryptocurrency using blockchain technology to enable transferring funds without the use of intermediaries such as banks, governments, agents or brokers. This means that, using the blockchain network, you can instantly send Bitcoin to anyone else across the globe.
What blockchain technology is Bitcoin built on? The Bitcoin blockchain is a public ledger that records Bitcoin transactions. It is implemented as a chain of blocks, each block containing a cryptographic hash of the previous block up to the genesis block in the chain. A network of communicating nodes running Bitcoin software maintains the blockchain.
The blockchain technology is a series of blocks linked together. The blocks store the data of recent transactions occurring on the network that are yet to be validated. These blocks represent an explicit encryption of a particular code authentication and are all connected together by chains. After a block has been verified by a miner, the block is closed and a new one is created for new transactions for miners to validate next.
To understand Bitcoin mining, you have to first understand the three major blockchain components:
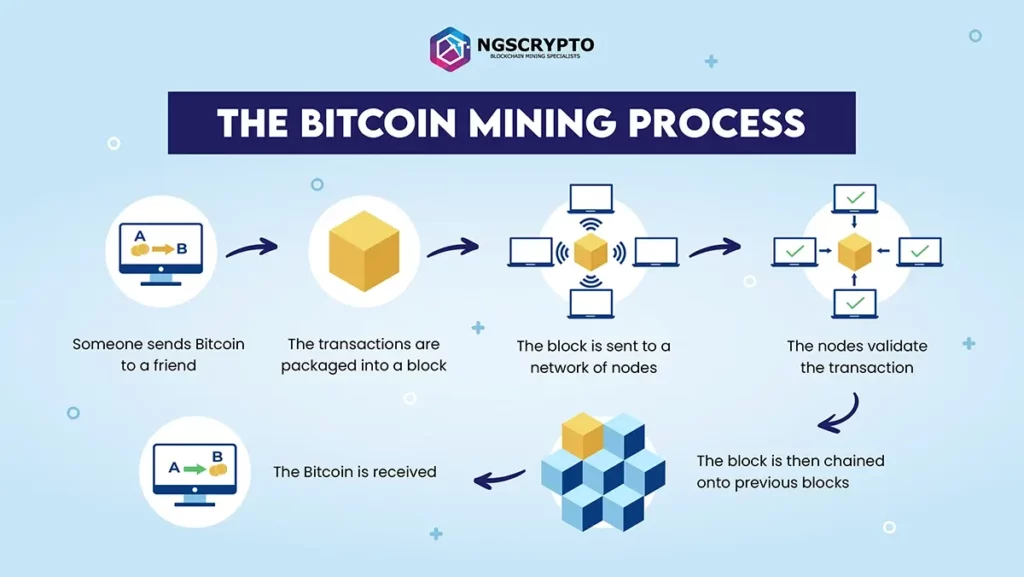
Before you invest time and equipment into mining, read this explainer to see how Bitcoin mining works step by step :
A Bitcoin miner will first select their tools of the trade and set them up. These include:
When a transaction is initiated in the Bitcoin network, three elements are involved:
Bitcoin mining software provides a unique cryptographic hash puzzle that is tough to decode for each transaction input. The software then constructs a Merkle tree based on the number of transactions required to constitute a block.
A Merkle tree is a data structure that contains all of the hashes in a block and serves as a summary of all transactions in the block. Hashes of individual transactions, known as transaction IDs, are paired repeatedly in the Merkle tree using the SHA-256 method until only one hash identifies the entire tree. The Merkle root or root hash is the name given to this hash. The Merkle tree allows for efficient transaction verification in the Bitcoin network.
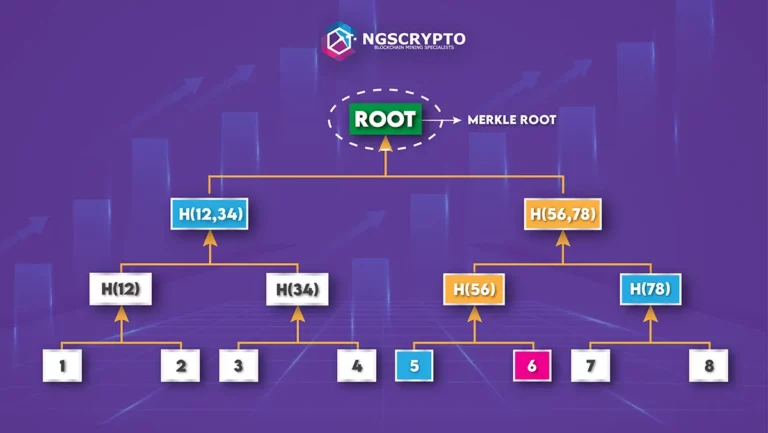
The block header contains the Merkle root, which is the identifier of a Merkle tree. The block header carries block information and includes the following components:
Miners will use this information to solve the hash problem and add a block transaction.
Miners must solve the hash problem by locating the hash that is less than a specific target using the difficulty requirement. The target, which is kept in the header, is a 67-digit number that determines the mining difficulty based on the amount of miners trying to solve a hash function. It is vital to remember that this difficulty adjusts after every 2016 block is created based on how long miners took to solve an equation in the previous 2016 blocks. This also contributes to keeping the rate of transaction appending in the blockchain at 10 minutes.
Miners will attempt to solve the hash problem by continuously adding a nonce to the block header until the hash value returned is less than the target. When a mining computer solves the puzzle, a new block is successfully created and validated in the Bitcoin network when nodes reach a consensus. When a block is validated, the transactions it contains are validated, and the block is added to the chain. As previously stated, this occurs every 10 minutes.
Because several miners (systems) will be vying to solve the puzzle, the first miner to obtain the proper hash value receives a Bitcoin prize. This technique enables for the circulation of more Bitcoins.
There are generally three basic components to a mining operation: the mining hardware, the wallet, and the equipment.
In order to remain competitive, miners must now invest in professional computer equipment such as a graphics processing unit (GPU) or, more realistically, an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). These can cost anywhere from $500 to tens of thousands of dollars.
This is where you will keep any Bitcoin you earn as a consequence of your mining activities. A wallet is a secure online account that allows you to store, send, and receive Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies.
This method necessitates technical knowledge, and you may need to conduct some research on the subject. If you want to connect many rigs, things can get a little complicated, but it’s not rocket science. If you lack command line experience, purchasing a mining device with a GUI (Graphic User Interface) that allows you to set up the hardware with a mouse will be beneficial.
A new Bitcoin is created approximately every 96 seconds, with a new block typically being created every 10 minutes. One Bitcoin can take a substantial amount of time for a miner to produce. As of May 11 2020, the price is 6.25 Bitcoins per block, and with 1 BTC is equal to $45,678.37 AUD (as of July 2023), the reward for validating a block is a sizeable sum. It’s important to note that, like all cryptocurrencies, the price of BTC is constantly fluctuating and influenced by events such as Bitcoin Halving which is due to occur again in 2024.

Bitcoin miners prioritise using the cheapest electricity available due to several reasons. Firstly, people create Bitcoin by using electricity and specialised mining machines called ASICs. These machines work all over the world and generate Bitcoin at a similar pace.
Miners sell the Bitcoin in a global marketplace and transfer it to buyers by updating a shared ledger. Miners can reduce their expenses by managing their electricity usage. Electricity costs make up about 70% of their overall expenses. By optimising their electricity usage, miners can increase their profits.
The facts mentioned above indicate that mining is moving towards utilising almost free energy. ASICs are widely available and uniform. Anyone who can perform Bitcoin mining at a cost less than its worth can effortlessly undertake it.
However, as more miners join the market, those with higher expenses will find it difficult to stay profitable. We will encourage miners who spend less than others to join, which will cause less skilled miners to leave.
The miners using cheaper energy have a competitive edge due to lower energy costs. If they can find 50% energy savings, their overall expenses will decrease by 35%, resulting in higher profit margins.
The electricity bill is the most important factor for miners. If their costs are high, they will have to close down and sell their assets. We will use cheaper energy sources instead. Other factors like firmware, cooling, taxes, personnel, access to capital, and uptime also matter.
Bitcoin miners prioritise using the cheapest electricity available due to several reasons. Firstly, people create Bitcoin by using electricity and specialised mining machines called ASICs. These machines work all over the world and generate Bitcoin at a similar pace.
Miners sell the Bitcoin in a global marketplace and transfer it to buyers by updating a shared ledger. Miners can reduce their expenses by managing their electricity usage. Electricity costs make up about 70% of their overall expenses. By optimising their electricity usage, miners can increase their profits.
The facts mentioned above indicate that mining is moving towards utilising almost free energy. ASICs are widely available and uniform. Anyone who can perform Bitcoin mining at a cost less than its worth can effortlessly undertake it.
However, as more miners join the market, those with higher expenses will find it difficult to stay profitable. We will encourage miners who spend less than others to join, which will cause less skilled miners to leave.
The miners using cheaper energy have a competitive edge due to lower energy costs. If they can find 50% energy savings, their overall expenses will decrease by 35%, resulting in higher profit margins.
The electricity bill is the most important factor for miners. If their costs are high, they will have to close down and sell their assets. We will use cheaper energy sources instead. Other factors like firmware, cooling, taxes, personnel, access to capital, and uptime also matter.
There are several ways to get involved in mining and crypto and YouTuber Drew Vosk has taken the time to analyse these methods. Drawing from his own experience, he assesses their feasibility and predicts their future success. In a video released on January 2, he shares that although GPU mining may no longer be profitable, there are still other ways to earn passive income with cryptocurrencies:
Vosk suggests that those who already have equipment generating a few dollars a day should continue using it. However, they should still analyse their options and compare electricity rates to find the most suitable choice.
Vosk’s experience offers an expert perspective on specialized mining methods. If you’re just starting out, gain a foundational understanding of mining methods to complement this expert advice.
Despite its wide acceptance worldwide, Bitcoin still sparks intense debate in some countries due to its decentralised nature, volatility, and extremely high power consumption. The legality of mining Bitcoins entirely depends on where you live. The dominance of fiat currencies and governmental control over the financial markets could be threatened by the idea of Bitcoin. Because of this, Bitcoin is wholly prohibited in several locations.
Most countries allow people to hold Bitcoins and engage in Bitcoin mining. The United States, Canada, Australia, and the UAE all accept Bitcoin and use it frequently. EU nations including Finland, Germany, France, and others also do. El Salvador is the only nation to have accepted Bitcoin as legal tender.
Due to intense competition and legal considerations, most Bitcoin miners collaborate in mining pools or engage a third party, such as a mining company like NGS Crypto.
NGS Crypto is an authorized Reseller of NGS Group, that offers Blockchain Mining Packages, Offering Returns Ranging From 6-16% Per Annum.
The information presented on this website is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind.
NGS Crypto is an authorised reseller of NGS Group blockchain mining packages. The information presented on this website (https://ngscrypto.com) is general information only. It should not be taken as constituting professional advice from the website owner – NGS Crypto PTY LTD (NGS Crypto). Any information regarding past performance and returns contained on this website should not be construed or interpreted as a prediction or opinion as to future performance and returns. NGS Crypto is not a financial adviser. All views and observations expressed by NGS Crypto on this website are for information purposes only, are general in nature and should not be treated as investment or financial advice of any kind. Before making an investment in crypto assets, you should consider seeking independent legal, financial, taxation or other such professional advice to check how the information on this website relates to your unique circumstances. NGS Crypto is not liable for any loss caused, whether due to negligence or otherwise arising from the use of, or reliance on, the information provided directly or indirectly, by use of this website. You can view our full terms & conditions by clicking here.
NGS Crypto is not affiliated, associated, authorized, endorsed by, or in any way officially connected with this NGS Super (ABN 73 549 180 515).
© 2024 NGS Crypto
NGS Crypto is an Authorised Reseller of NGS Group
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |